From India's continued preference for male children to impact of climate change on Indian agriculture, the Economic Survey 2018 highlights 10 important facts about the Indian economy. For the first time in India‘s history, data on international exports of states has also been dwelt upon in the Economic Survey.
Here are the ten facts:
1. There has been a large increase in registered indirect and direct taxpayers. There is a 50 per cent increase in unique indirect taxpayers under the GST compared with the pre-GST system. There has also been an addition (over and above trend growth) of about 1.8 million in individual income tax filers since November 2016.
2. Formal non-agricultural payroll is much greater than believed. The number is more than 30 per cent when formality is defined in terms of social security, such as EPFO/ESIC savings, and more than 50 per cent when defined in terms of being in the GST net.
3. States' prosperity is correlated with their international and inter-state trade. The more the state exports and trade with other states, the more prosper it is. The correlation is even stronger between prosperity and international trade.
4. India's firm export structure is substantially more egalitarian than in other large countries. The top one per cent of Indian firms account for only 38 per cent of exports compared with 72, 68 and 55 per cent in Brazil, Germany and the US, respectively.
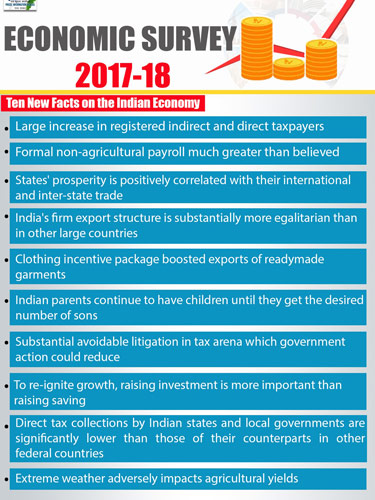
5. It was pointed out that the Rebate of State Levies (ROSL) has increased exports of readymade garments (man-made fibers) by about 16 per cent but not of others.
6. The data highlighted another seemingly known fact that Indian society exhibits a strong desire for a male child. It pointed out that most parents continued to have children until they get a number of sons.
7. The survey pointed out that tax departments in India have gone in for contesting in several tax disputes but also with a low success rate, which is below 30 per cent. About 66 per cent of pending cases accounted for only 1.8 per cent of the value at stake. It further stated that 0.2 per cent of cases accounted for 56 per cent of the value at stake.
8. Extrapolating the data, the survey indicated that raising investment is more important than increasing savings to re-ignite growth. Growth in savings did not bring economic growth but the growth in investment did.
9. The survey mentions that collections of direct taxes by Indian states and other local governments, where they have powers to collect them, is significantly lower than their counterparts in other federal countries. A comparison has been given between ratios of direct tax to total revenues of local governments in India, Brazil and Germany.
10. The survey captures the footprints of climate change on the Indian territory and consequent adverse impact on agricultural yields. Extreme temperature increases and deficiency in rainfall have been captured on the Indian map and the graphical changes in agricultural yields are brought out from such data. The impact was found to be twice as large in un-irrigated areas as in irrigated ones.





