ISL side Kerala Blasters lined up for their match against Punjab FC sans their captain and star midfielder Adrian Luna. Amidst speculations about the 31-year-old Urugayan's fitness, KBFC confirmed in a club statement on Saturday that Luna underwent "a minor arthroscopic surgery for the treatment of a chondral knee injury."
A footballer is likely to receive a chondral injury due to a fall, an ankle twist or even taking a direct tackle to the knee -- all possible during a practice session.
The Manjappada remain concerned as the club didn't reveal when Adrian Luna is going to get match fit after rehabilitation.
Our ©aptain sends his heartfelt gratitude to all well wishers for their love and unwavering support! 💛📽️#KBFC #KeralaBlasters pic.twitter.com/JnQhGMV9u9
— Kerala Blasters FC (@KeralaBlasters) December 16, 2023
Here is explaining everything that football fans should know about arthroscopic surgery
1. The process: Arthroscopic surgery is an equipment-dependent surgery. When professional sportsmen suffer career-threatening injuries to the joints, particularly on the knee and shoulder, surgeries are carried out arthroscopically. The modern surgery method is such that the patient can literally walk into the operation theatre and walk out of it.
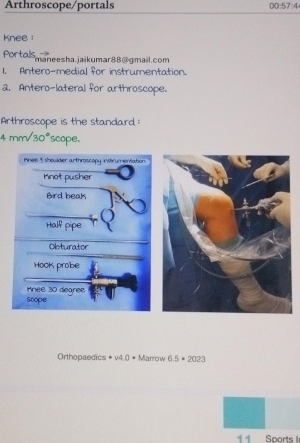
In simple terms, the surgical procedure is done by inserting a small camera and instruments into the knee to perform surgery inside the joint. The surgeons, using these instruments remove loose or damaged cartilage.
2. The knee joint, shoulder joint, ankle joint, wrist and elbow are the areas where arthroscopic surgeries are done.
3. Surgical tools involved: Surgeons use basic hand instruments including probes, cutters, graspers, scissors, knives etc.
In case of complex arthroscopic operations, instruments such as motorized shaver, underwater cutting cautery etc are needed. Some special instruments are required for particular operations such as ACL, PCL reconstructions.
4. An arthroscope: It is a 4 mm telescope having a 30° forward oblique angle. This obliquity helps in increasing the field of vision. However, a smaller size arthroscope is used for smaller joints.
Apart from the arthroscope, a light source, fibre-optic cable, video camera and TV monitor and also needed to visualise inside the joint.
5. Diagnostic arthroscopy: Arthroscopy is a technique of surgery on the joints in which the tip of a thin (4 mm diameter) telescope called "arthroscope" is introduced into a joint, and the inside of the joint is examined.
6. Arthroscopic surgery: Once the diagnosis is made, necessary corrections are done right away, by introducing micro-instruments through another small skin puncture. This procedure is called arthroscopic surgery.
ADVANTAGES OF ARTHROSCOPIC SURGERY
7. Minimally invasive technique: The operation is performed through small punctures, without cutting open the joint. Thus, there is almost no blood loss.
8. Day-care surgery: This means that the patient is admitted on the morning of the operation and sent home the same evening.
🚨 𝐈𝐧𝐣𝐮𝐫𝐲 𝐔𝐩𝐝𝐚𝐭𝐞: 𝐀𝐝𝐫𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐋𝐮𝐧𝐚
— Kerala Blasters FC (@KeralaBlasters) December 16, 2023
The Club would like to update that, Adrian Luna successfully underwent a minor arthroscopic surgery for the treatment of a chondral knee injury after which he is currently in the process of rest and recovery towards full… pic.twitter.com/a5blQIFfJH
9. Little immobilisation required: The only immobilisation of the knee is in the form of a small dressing for 48 hours. It allows the knee to be bent and it allows the patient to be up and about in the house within 48 hours.
In most cases, the patient requires no physiotherapy.
10. Barely visible scars: Since the whole operation is performed through multiple small punctures, the scars are barely visible.
Source: 1. 'Essential Orthopaedics Including Clinical Methods' by Maheshwari and Mhaskar
2. melbournehipandknee.com.au