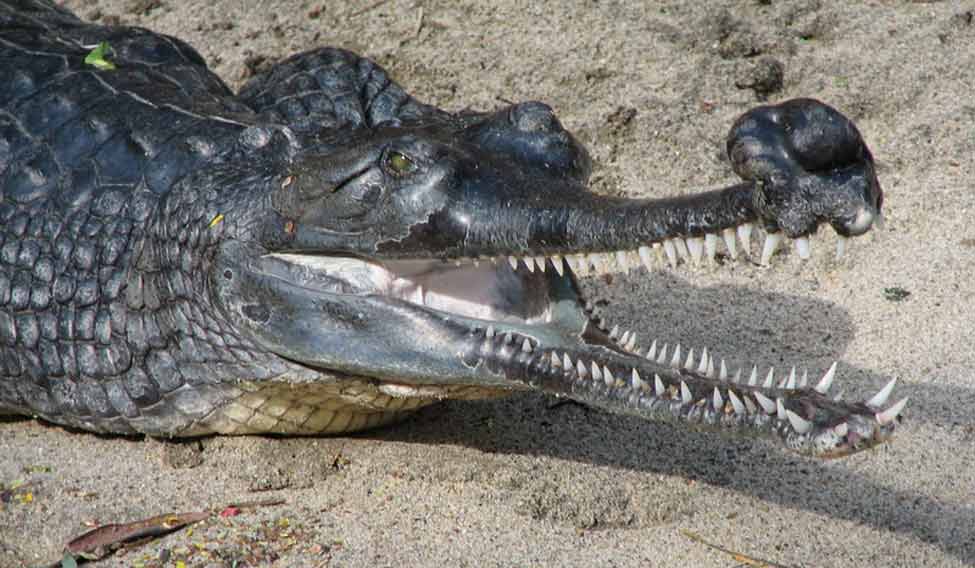
Born under captivity in Patna Zoo, a young critically-endangered gharial who was released into the wild has now lost her freedom once again after swimming 1,000 kilometres into the neighbouring West Bengal.
The nine-year-old sub-adult female gharial was released in the Gandak river near Valmiki Tiger Reserve last year along with 24 other crocodiles by the Bihar forest department as part of a conservation programme.
For reasons best known to nature, the gharial swam over 1,000km over the next few months to reach Mahananda river which flows in the northern part of West Bengal. Gandak and Mahananda are both interconnected through the river Ganga as its tributaries.
In Malda district local fishermen raised an alarm after spotting the gharial as they felt threatened by it. West Bengal forest department officials then captured it and kept it at Rasik Bill in Cooch Behar last October.
The release of the crocodile has now become complicated since it is a trans-state issue.
“This is not good for the animal. It has survived so long in nature after being in captivity for eight years. Now it is a wild animal and if it is forced to return to captivity then you are spoiling its life. We had released it in the wild so that biodiversity increases in the river,” Wildlife Trust of India (WTI)’s Samir Kumar Sinha said.
He is working along with the Bihar forest department to save the gharials from extinction as it is estimated that only about 200 breeding individuals of the species, listed as critically endangered, survive in the wild today.